Research
Interactive Image Segmentation via Backpropagating Refinement Scheme
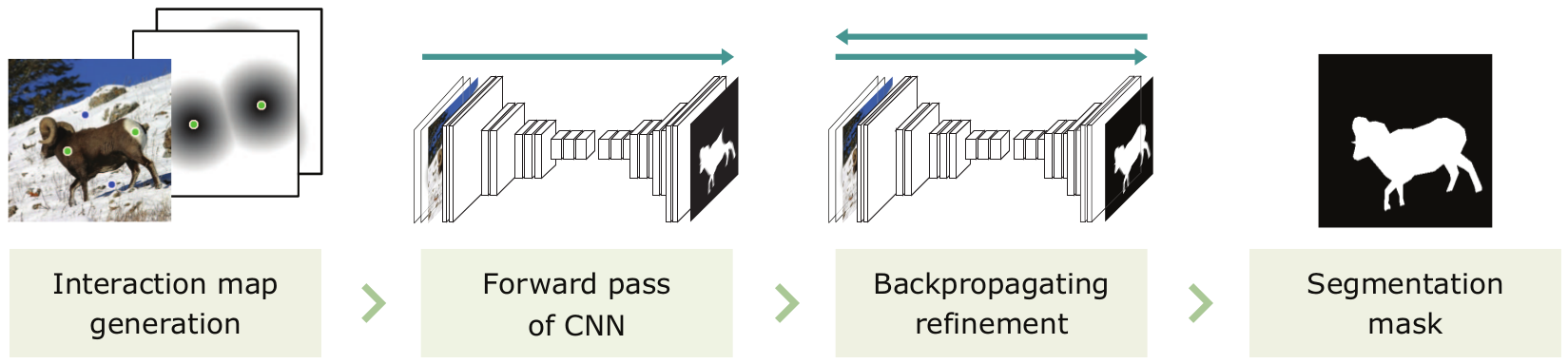
Abstract
An interactive image segmentation algorithm, which accepts user-annotations about a target object and the background, is proposed in this work. We convert user-annotations into interaction maps by measuring distances of each pixel to the annotated locations. Then, we perform the forward pass in a convolutional neural network, which outputs an initial segmentation map. However, the user-annotated locations can be mislabeled in the initial result. Therefore, we develop the backpropagating refinement scheme (BRS), which corrects the mislabeled pixels. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm outperforms the conventional algorithms on four challenging datasets. Furthermore, we demonstrate the generality and applicability of BRS in other computer vision tasks, by transforming existing convolutional neural networks into user-interactive ones.
Publication
Won-Dong Jang and Chang-Su Kim, “Interactive Image Segmentation via Backpropagating Refinement Scheme,” in Proc. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019. [pdf] [supplementary video]
Code
Online Video Object Segmentation via Convolutional Trident Network
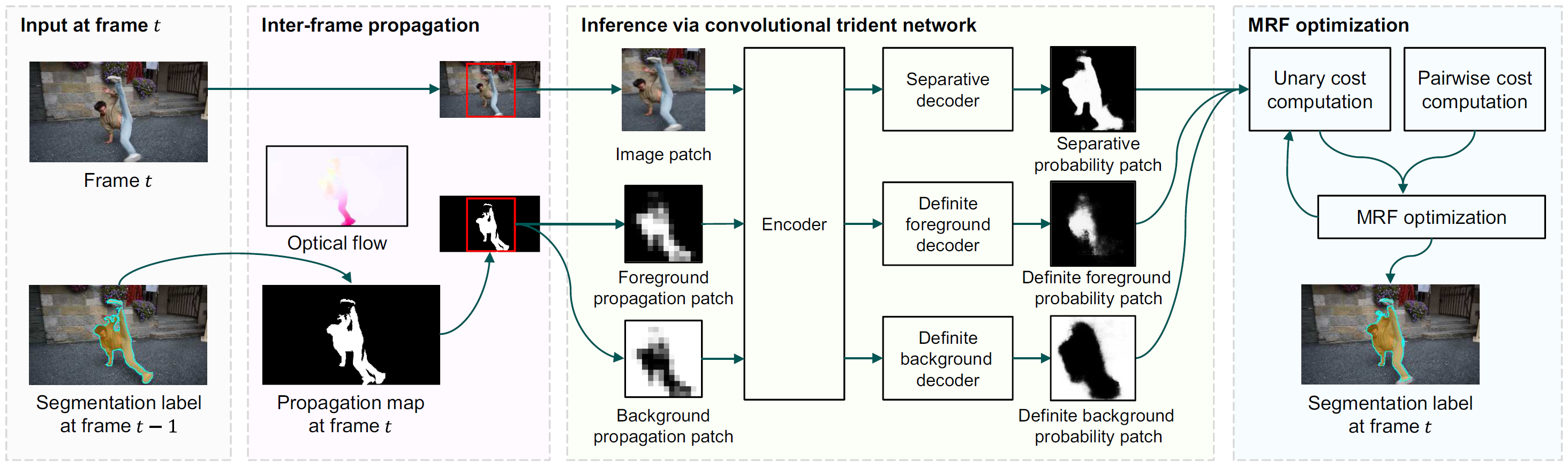
Abstract
A semi-supervised online video object segmentation algorithm, which accepts user annotations about a target object at the first frame, is proposed in this work. We propagate the segmentation labels at the previous frame to the current frame using optical flow vectors. However, the propagation is error-prone. Therefore, we develop the convolutional trident network (CTN), which has three decoding branches: separative, definite foreground, and definite background decoders. Then, we perform Markov random field optimization based on outputs of the three decoders. We sequentially carry out these processes from the second to the last frames to extract a segment track of the target object. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art conventional algorithms on the DAVIS benchmark dataset.
Publication
Won-Dong Jang and Chang-Su Kim, “Online Video Object Segmentation via Convolutional Trident Network,” in Proc. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, pp. 5849-5858, Jul. 2017. [pdf] [supplementary video]
Code
Streaming Video Segmentation via Short-Term Hierarchical Segmentation and Frame-by-Frame Markov Random Field Optimization
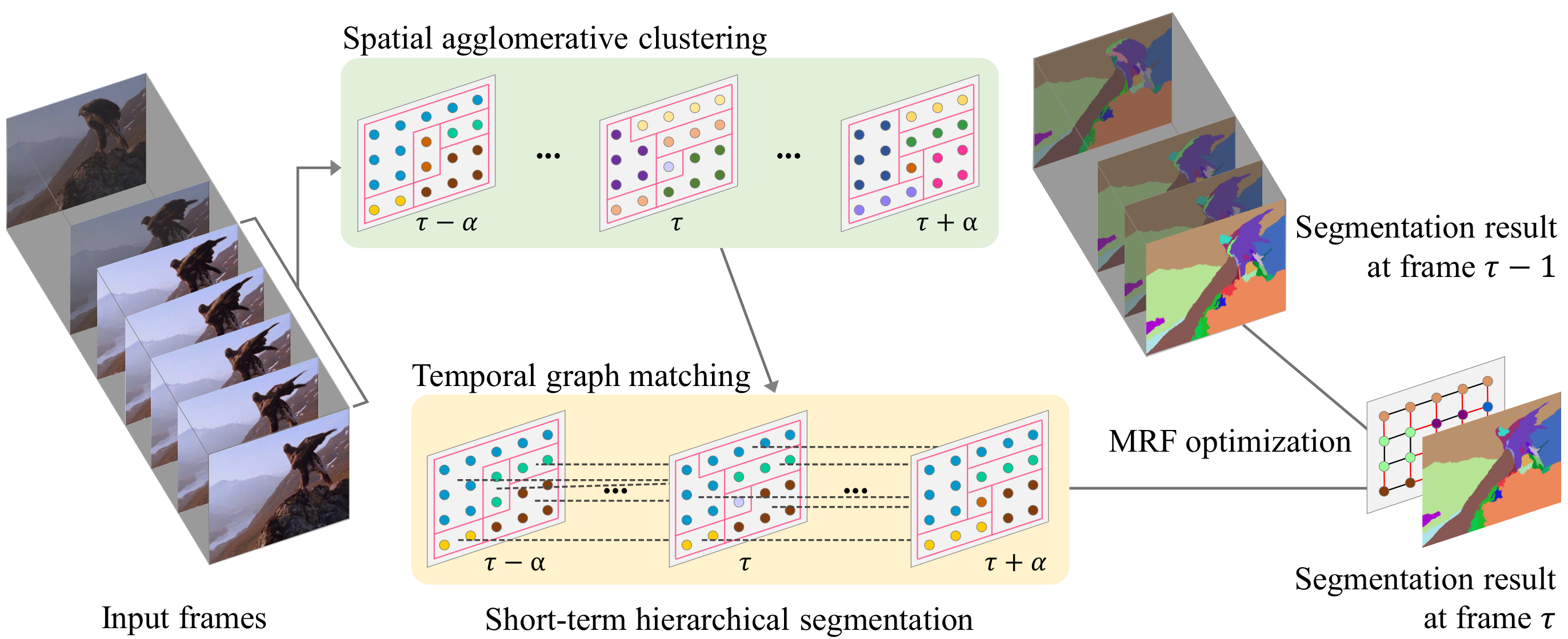
Abstract
An online video segmentation algorithm, based on short-term hierarchical segmentation (STHS) and frame-by-frame Markov random field (MRF) optimization, is proposed in this work. We develop the STHS technique, which generates initial segments by sliding a short window of frames. In STHS, we apply spatial agglomerative clustering to each frame, and then adopt inter-frame bipartite graph matching to construct initial segments. Then, we partition each frame into final segments, by minimizing an MRF energy function composed of unary and pairwise costs. We compute the unary cost using the STHS initial segments and the segmentation result at the previous frame. We set the pairwise cost to encourage similar nodes to have the same segment label. Experimental results on a video segmentation benchmark dataset, VSB100, demonstrate that the proposed algorithm outperforms state-of-the-art online video segmentation techniques significantly.
Publication
Won-Dong Jang and Chang-Su Kim, “Streaming Video Segmentation via Short-Term Hierarchical Segmentation and Frame-by-Frame Markov Random Field Optimization,” in Proc. European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, Netherlands, Oct. 2016. [pdf]
Code
Semi-supervised Video Object Segmentation Using Multiple Random Walkers

Abstract
A semi-supervised video object segmentation algorithm using multiple random walkers (MRW) is proposed in this work. We develop an initial probability estimation scheme that minimizes an objective function to roughly separate the foreground from the background. Then, we simulate MRW by employing the foreground and background agents. During the MRW process, we update restart distributions using a hybrid of inference restart rule and interactive restart rule. By performing these processes from the second to the last frames, we obtain a segment track of the target object. Furthermore, we optionally refine the segment track by performing Markov random field optimization. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art conventional algorithms on the SegTrack v2 dataset.
Publication
Won-Dong Jang and Chang-Su Kim, “Semi-supervised Video Object Segmentation Using Multiple Random Walkers,” in Proc. British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), York, UK, Sep. 2016. [pdf]
Code
Primary Object Segmentation in Videos via Alternate Convex Optimization of Foreground and Background Distributions

Abstract
An unsupervised video object segmentation algorithm, which discovers a primary object in a video sequence automatically, is proposed in this work. We introduce three energies in terms of foreground and background probability distributions: Markov, spatiotemporal, and antagonistic energies. Then, we minimize a hybrid of the three energies to separate a primary object from its background. However, the hybrid energy is nonconvex. Therefore, we develop the alternate convex optimization (ACO) scheme, which decomposes the nonconvex optimization into two quadratic programs. Moreover, we propose the forward-backward strategy, which performs the segmentation sequentially from the first to the last frames and then vice versa, to exploit temporal correlations. Experimental results on extensive datasets demonstrate that the proposed ACO algorithm outperforms the state-of-the-art techniques significantly.
Publication
Won-Dong Jang, Chulwoo Lee, and Chang-Su Kim, “Primary Object Segmentation in Videos via Alternate Convex Optimization of Foreground and Background Distributions,” in Proc. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, pp. 696-704, Jun. 2016. [pdf] [supplementary video]
